At present, industrial robots have been widely used in all walks of life, but we also found that industrial robots not only have different shapes, but also have different numbers of axes. The so-called axis of industrial robot can be explained by the professional term degree of freedom. If the robot has three degrees of freedom, it can move freely along the X, y and Z axes, but it can’t tilt or rotate. When the number of axes of the robot increases, it is more flexible for the robot. How many axes should industrial robots have?
Three axis robot is also called Cartesian coordinate or Cartesian robot. Its three axes can allow the robot to move along the three axes. This kind of robot is generally used in simple handling work.
Four axis robot can rotate along X, y and Z axes. Different from three-axis robot, it has an independent fourth axis. Generally speaking, SCARA robot can be considered as four axis robot.
Five axis is the configuration of many industrial robots. These robots can rotate through three space cycles of X, y and Z. at the same time, they can turn around by relying on the axis on the base and the axis with flexible rotation of the hand, which increases their flexibility.
The six axis robot can pass through the X, y and Z axes, and each axis can rotate independently. The biggest difference from the five axis robot is that there is an additional axis that can rotate freely. The representative of the six axis robot is youao robot. Through the blue cover on the robot, you can clearly calculate the number of axes of the robot.
Seven axis robot, also known as redundant robot, compared with six axis robot, the additional axis allows the robot to avoid some specific targets, facilitate the end effector to reach a specific position, and can more flexibly adapt to some special working environment.
With the increase of the number of axes, the flexibility of the robot also increases. However, in the current industrial applications, three-axis, four-axis and six axis industrial robots are used most. This is because in some applications, high flexibility is not required, three-axis and four-axis robots have higher cost-effectiveness, and three-axis and four-axis robots also have great advantages in speed.
In the future, in the 3C industry that needs high flexibility, the seven axis industrial robot will have a place to play. With its increasing accuracy, it will replace manual assembly of precision electronic products such as mobile phones in the near future.
What is the advantage of seven axis industrial robot over six axis industrial robot?
Technically, what are the problems with six axis industrial robots and what are the strengths of seven axis industrial robots?
(1) Improve kinematic characteristics
In the kinematics of robot, three problems make the motion of robot very limited.
The first is the singular configuration. When the robot is in a singular configuration, its end effector can not move in a certain direction or apply torque, so the singular configuration greatly affects the motion planning.
The sixth axis and the fourth axis of the six axis robot are collinear
The second is joint displacement overrun. In the real working situation, the angle range of each joint of the robot is limited. The ideal state is plus or minus 180 degrees, but many joints can’t do it. In addition, the seven axis robot can avoid too fast angular velocity movement and make the angular velocity distribution more uniform.
Motion range and maximum angular velocity of each axis of Xinsong seven axis robot
Third, there are obstacles in the working environment. In the industrial environment, there are various environmental obstacles in many occasions. The traditional six axis robot can not only change the attitude of the end mechanism without changing the position of the end mechanism.
(2) Improve dynamic characteristics
For the seven axis robot, using its redundant degrees of freedom can not only achieve good kinematic characteristics through trajectory planning, but also use its structure to achieve the best dynamic performance.
The seven axis robot can realize the redistribution of joint torque, which involves the problem of static balance of the robot, that is, the force acting on the end can be calculated by a certain algorithm. For the traditional six axis robot, the force of each joint is certain, and its distribution may be very unreasonable. However, for the seven axis robot, we can adjust the torque of each joint through the control algorithm to make the torque borne by the weak link as small as possible, so that the torque distribution of the whole robot is more uniform and more reasonable.
(3) Fault tolerance
In case of failure, if one joint fails, the traditional six axis robot can not continue to complete the work, while the seven axis robot can continue to work normally by readjusting the redistribution of the speed of the failed joint (kinematic fault tolerance) and the torque of the failed joint (dynamic fault tolerance).
Whether from the product point of view or from the application point of view, the seven axis industrial robot is still in the preliminary development stage, but major manufacturers have pushed relevant products in major exhibitions. It can be imagined that they are very optimistic about its future development potential.
-KUKA LBR iiwa
In November 2014, KUKA first released KUKA’s first 7-DOF light sensitive robot lbriiwa at the robot exhibition of China International Industry Expo.
Lbriiwa seven axis robot is designed based on human arm. Combined with integrated sensor system, the light robot has programmable sensitivity and very high accuracy. All the axes of the seven axis lbriiwa are equipped with high-performance collision detection function and integrated joint torque sensor to realize man-machine cooperation.
The seven axis design makes KUKA’s product have high flexibility and can easily cross obstacles. The structure of lbriiwa robot is made of aluminum, and its own weight is only 23.9 kg. There are two kinds of loads, 7 kg and 14 kg respectively, making it the first light robot with a load of more than 10 kg.
- ABB YuMi
On April 13, 2015, abb officially launched the world’s first dual arm industrial robot Yumi that truly realizes man-machine cooperation to the market at the Industrial Expo in Hanover, Germany
Each single arm of Yumi has seven degrees of freedom and the body weight is 38 kg. The load of each arm is 0.5kg, and the repeated positioning accuracy can reach 0.02mm. Therefore, it is especially suitable for small parts assembly, consumer goods, toys and other fields. From the precision parts of mechanical watches to the processing of mobile phones, tablet computers and desktop computer parts, Yumi is no problem, which reflects the excellent characteristics of the redundant robot, such as expanding the reachable workspace, flexibility, agility and accuracy.
-Yaskawa Motoman SIA
YASKAWA electric, a well-known robot manufacturer in Japan and one of the “four families”, has also released a number of seven axis robot products. SIA series robots are light agile seven axis robots, which can provide humanoid flexibility and accelerate quickly. The lightweight and streamlined design of this series of robots makes it very suitable for installation in a narrow space. SIA series can provide high payload (5kg to 50kg) and large working range (559mm to 1630mm), which is very suitable for assembly, injection molding, inspection and other operations.
In addition to the light seven axis robot products, Yaskawa has also released the seven axis robot welding system. Its high degree of freedom can maintain the most suitable posture as far as possible to achieve high-quality welding effect, especially suitable for inner surface welding and achieve the best approach position. Moreover, the product can have a high-density layout, easily avoid the interference between it and the shaft and workpiece, and show its excellent obstacle avoidance function.
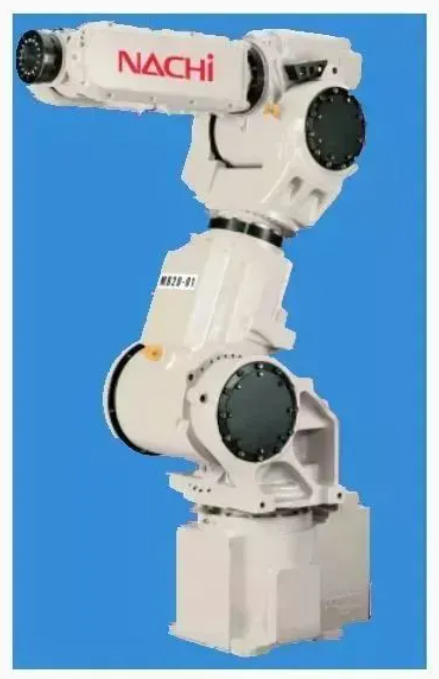
-The more intelligent, the more Presto mr20
As early as the end of 2007, Na bueryue developed the seven degree of freedom robot “Presto mr20″. By adopting the seven axis design, the robot can perform more complex workflow and move in a narrow working area like a human arm. In addition, Robot front end The torque of (wrist) is about twice that of the original traditional six axis robot. The torque of the standard configuration is 20kg. By setting the action range, it can carry up to 30kg of articles, the working range is 1260mm, and the repeated positioning accuracy is 0.1mm. By adopting the seven axis structure, mr20 can work from the side of the machine tool when taking and placing workpieces on the machine tool. In this way, It improves the efficiency of preparation and maintenance in advance. The space between machine tools can be reduced to less than half of the traditional six axis robot.
In addition, nazhibueryue has also released two industrial robots, mr35 (with a load of 35kg) and mr50 (with a load of 50kg), which can be used in narrow spaces and places with obstacles.
-OTC seven axis industrial robot
Odish of daihen group in Japan has launched the latest seven axis robots (fd-b4s, fd-b4ls, fd-v6s, fd-v6ls and fd-v20s). Due to the rotation of the seventh axis, they can realize the same twisting action as human wrists and welding for more than one week; in addition, seven axis robots are human (fd-b4s, fd-b4ls) the welding cable is hidden in the robot body, so there is no need to pay attention to the interference between the robot, the welding fixture and the workpiece during the teaching operation. The action is very smooth, and the degree of freedom of welding posture has been improved, which can make up for the defect that the traditional robot cannot enter the welding due to the interference with the workpiece or welding fixture.
-Baxter and Sawyer of rethink Robotics
Rethink robotics is a pioneer of cooperative robots. Among them, Baxter dual arm robot, which was first developed, has seven degrees of freedom on both arms, and the maximum working range of one arm is 1210mm. Baxter can process two different tasks at the same time to increase applicability, or process the same task in real time to maximize output.
Sawyer, launched last year, is a single arm seven axis robot. Its flexible joints use the same series elastic actuator, but the actuator used in its joints has been redesigned to make it smaller. Because the seven axis design is adopted and the working range is extended to 100mm, it can complete the work task with larger load, and the load can reach 4kg, which is much larger than the 2.2kg payload of Baxter robot.
-Yamaha seven axis robot Ya series
In 2015, Yamaha launched three seven axis robots “ya-u5f”, “ya-u10f” and “ya-u20f”, which are driven and controlled by the new controller “ya-c100″.
The 7-axis robot has an e-axis equivalent to human elbow, so it can freely complete bending, torsion, extension and other actions. Even in the narrow gap where it is difficult for the robot to perform the operation below 6 axes, the operation and setting can be completed smoothly. In addition, it can also realize the low squat position and the action of winding around the back of the device. The actuator with hollow structure is adopted, and the device cable and air hose are built in the mechanical arm, which will not interfere with the surrounding equipment and can realize a compact production line.
Post time: Dec-27-2021